Cell Wall Disruption of Rape Bee Pollen Treated with Combination of Protamex Hydrolysis and Ultrasonication
Date:2015-09-14

Abstract
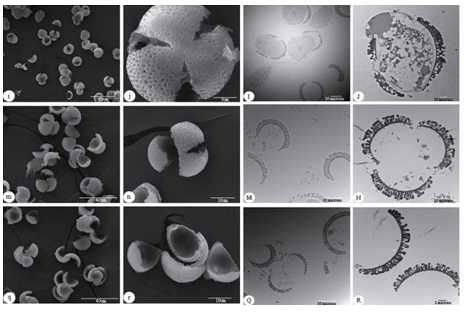
Bee pollen possesses a broad range of potential biological activities, but nutrient absorption and biological activities of bee pollen may be restricted due to complex pollen wall. This study aimed to investigate wall-disruption variations of Brassica campestris L. (rape) bee pollen treated with protamex hydrolysis, ultrasonication, and combination of protamex hydrolysis and ultrasonication. Pollen sample treated with these three treatments had higher specific surface area values and smaller particle sizes than the untreated sample. Protamex hydrolysis degraded the pollen coat and disintegrated the intine at the germinal apertures. Ultrasonication treatment cracked the pollen exine into fragments, but seemed to have little effect on the intine. The combination of protamex hydrolysis and ultrasonication can degrade pollen coat and entirely disrupt both the exine and the intine. The exine of rape bee pollen was disrupted into three fragments along germinal apertures.
Keywords: Rape bee pollen; Cell wall disruption; Combination of protamex; hydrolysis and ultrasonication; Scanning electron microscope; Transmission electron microscope.
This work has been published online on Food Research International, Volume 75, September 2015, Pages 123–130.
More details are available on the link bellow:http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0963996915300259