Research on Molecular Mechanism of 10-Hydroxydec-2-Enoic Acid against Cellular Oxidative Damage
Date:2022-07-06
Recently, Institute of Apicultural Research, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences found that 10-Hydroxydec-2-enoic acid (10-HDA), the iconic component of royal jelly, has the function of scavenging hydroxyl free radical (·OH) and reducing oxidative damage to cells. Related research results were published in Frontiers in Nutrition.
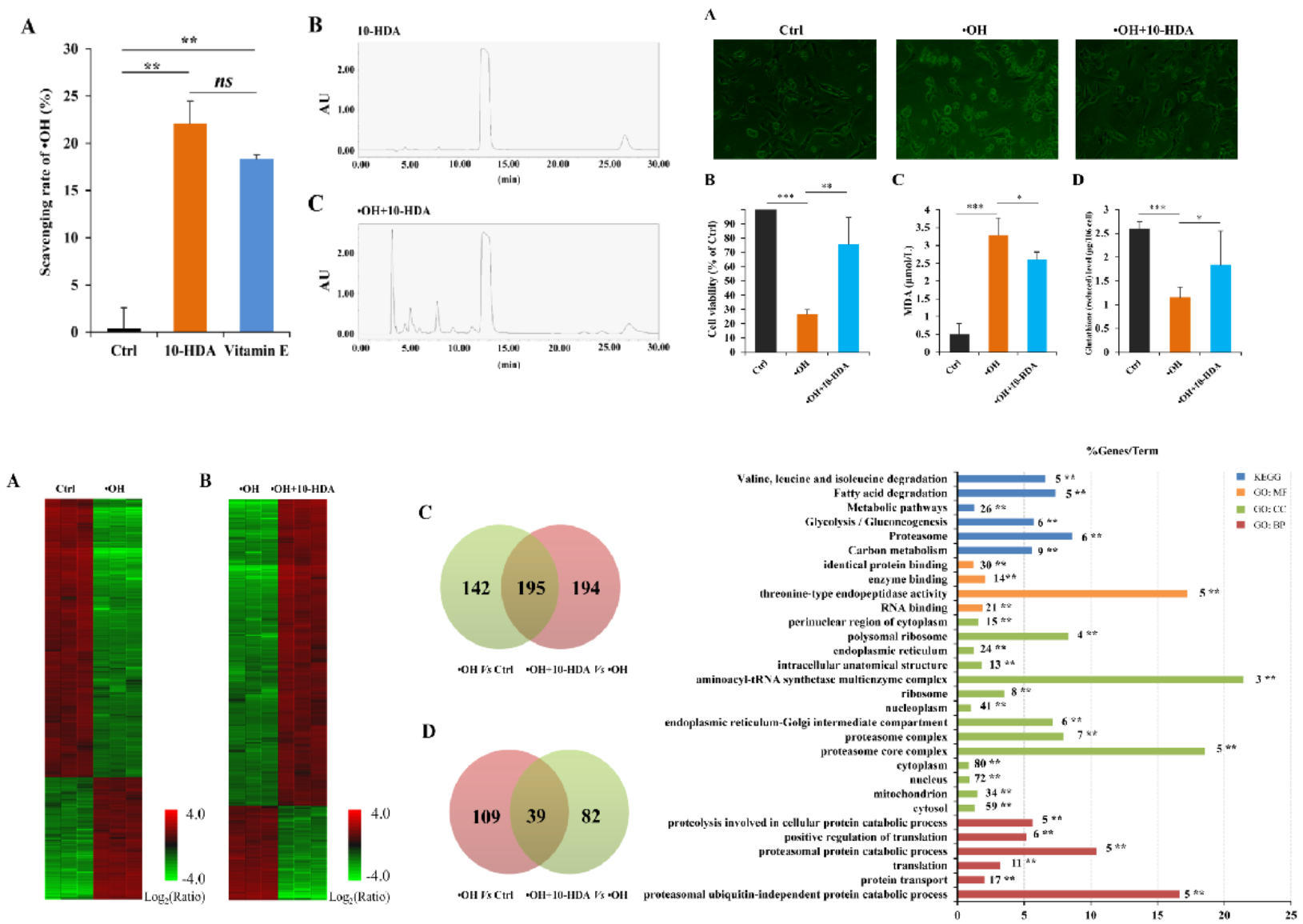
The reported studies show that 10-HDA has a series of health care effects and medicinal values including preventing cell and tissue photoaging damage induced by ultraviolet irradiation, alleviating lipopolysaccharide (LPS) -induced blood-brain barrier damage, and inhibiting cyclophosphamide-induced damage to immune organs, etc. However, the molecular mechanisms remain largely unknown. This research found that 10-HDA can react with·OH, thereby neutralizing it. On this basis, using hydroxyl radical-damaged mouse vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMC) as a model, it was found that 10-HDA can reduce the damage of ·OH to VSMC, improve cell viability, enhance cellular protein synthesis and transport at the molecular level as well as maintain protein stability and energy metabolism levels. In conclusion, this study revealed the significant molecular mechanism of 10-HDA against cellular oxidative damage and provided a theoretical basis for the application of 10-HDA and royal jelly in vascular health care.
Link:https://doi.org/10.3389/fnut.2022.873892