A Study on Allergens in Brassia Campestris L. Bee Pollen and Desensitization Mechanisms of Enzymatic Treatment
Date:2022-08-31
Institute of Apicultural Research of Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences made significant progress in the study on identifying allergens in Brassia campestris L. bee pollen and the desensitization mechanisms of enzymatic treatment recently. Relevant achievements were published online in Food Research International.
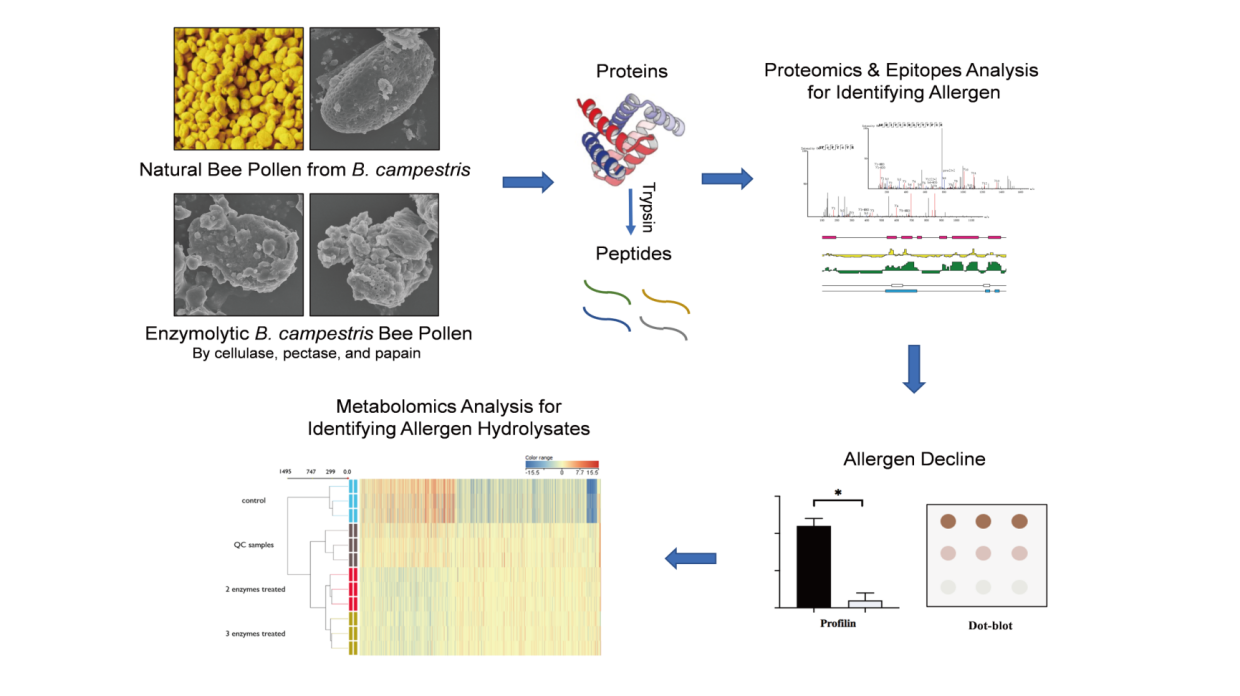
Bee pollen is a type of mass formed by honey bees adding nectar and salivary gland secretions to pollen grains they collect. Bee pollen boast abundant nutritional components, with extremely high edible and medicinal values. However, bee pollen has potential allergens and sensitization risk, which are constraints on the development and utilization of bee pollen to some extent. In this study, Brassia campestris L. bee pollen was desensitizedwith pectinase, cellulase and papain. Afterwards, five potential allergens, namely profilin, cystatin, alcohol dehydrogenase, prolamin, and expansin, were identified in samples by the mass spectrum-based proteomics analysis, and their antigenic epitopes were predicted by the bioinformatics method. According to the metabolomic analysis for Brassia campestris L. bee pollen, enzyme-treated bee pollen samples showed a significant reduction in three potentially allergenic proteins, namely profilin, cystatin and alcohol dehydrogenase, and a significant increase in oligopeptides and amino acids in principal components, compared with samples without enzymatic treatment. The results of Western blot showed a significant reduction in the binding capacity between bee pollen proteins extracted after enzymatic treatment and specific immunoglobulin antibodies, suggesting a remarkable decrease in the sensitization of Brassia campestris L. bee pollen after enzymatic treatment.
The study proved that the treatment with complex enzymes significantly reduced the sensitization of Brassia campestris L. bee pollen with a positive effect on its nutritive peculiarity, providing a scientific basis for improving the safety of bee pollen products and promoting their wide applications.
Link: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2022.111572